Hindi Is an Awesome Language
Hindi isn’t just an extremely fascinating language with a rich history. It’s also very important. It’s one of the most widely spoken languages in the world. And, most importantly, it ties the nation of India together. Why is that so crucial? Discover the history, current use, writing system, and grammar of the Hindi language.
Hindustani: Is It Hindi or Urdu?
Hindustani is the common name of both Hindi and Urdu. There’s a lot of heated debate about whether these two languages are the same or different. Well, they’re divided and connected at the same time by their history.
Hindi and Urdu used to be the same language. This Hindustani was the common language in the region that is Northern India for hundreds of years. But, they use different scripts in their writing, and some vocabulary is also different. However, they’re still largely mutually intelligible.
In this post, we’re going to focus on the Hindi language. But, we’ll take a look into the divide of Hindi and Urdu, and their shared history as well.
Basic Facts About Hindi
As I mentioned before, Hindi is very widely spoken. There are 425 million native Hindi speakers and 120 million people who speak it as a second language. Although, this number varies depending on how you count Urdu native and second-language speakers. But, overall, Hindi the third most widely spoken language in the world.
Hindi is an official language in India, Nepal, and Fiji. It is also widely spoken in Mauritiana, South Africa, and there are Hindi speaking communities in the United States too.
How Many Languages Are There In India?
India on a national level has two official languages: Hindi and English. But, each of the 22 states in the country can choose their own official languages. All-in-all, there are 23 official languages in India:
Assamese |
Bengali |
Bodo |
Dogri |
English |
Gujarati |
Hindi |
Kannada |
Kashmiri |
Konkani |
Maithili |
Malayalam |
Marathi |
Meitei |
Nepali |
Odia |
Punjabi |
Sanskrit |
Santali |
Sindhi |
Tamil |
Telugu |
Urdu |
But, of course, these are only the official languages. The minority languages, regional dialects, and language variations aren’t represented here. And, finding concrete numbers is very difficult, as different sources quote different figures.
According to Ethnologue, there are 448 distinct languages in India. Meanwhile, the People’s Linguistic Survey of India identified 780. And if you ask locals, they can list 19569 languages as their mother tongue according to the 2018 census. Of course, that’s only because different communities may call their language by a different name than another, even though they speak the same language.
The point is, there are a lot of languages in India. And these vary by accents, dialects, and different regions, towns, and cities have different words for everyday things. But, they’re all connected by Hindi. And that’s exactly why studying Hindi is so important.
What Language Family Is Hindi In?
Hindi is part of the Indo-European language family. Of this, it originates from the Indo-Arystan, Sanskrit, and finally the Sauraseni Prakrit branches.

The History of the Hindi Language
From its name, you can already see that Hindustani originates from the area surrounding the Indus River. This is part of Northern India and Pakistan today. As we’ve said before, Hindi is an Indo-Arystan language that developed from the Sauraseni Prakrit branch.
The Hindi or Hindustani language started to develop between the 7th and the 13th century CE. At this time there was a lot of Islamic and Arabic influence in the region because of Turkic and Arabic conquests. In the 13th century, the Delhi Sultanate further expanded the reach of the Islamic religion across the peninsula.
The Delhi Sultanate was a Muslim state ruled by Turkic and Afghan Dynasties. During its reign, the official language was Persian. But, in and around Delhi everyday people spoke Hindi. However, this Persian influence definitely changed the Hindustani language.
The Delhi Sultanate was followed by yet another Persianized empire called the Mughals (1605-1707). So, essentially from the 13th to the early 18th century, Persian was the official language on the Sub-Indian continent. In fact, it was also the lingua franca and the literary language. But, Hindustani was still used by everyday people.
By the end of the Mughal Empire, Hindustani became the language of the elite too. And under British rule, Hindustani became the official language of India alongside English, which it still is today.
Why the Urdu and the Hindi Writing System Is Different
Apart from Persian, Arabic was also a big influence because it’s the liturgical language of Islam. But, since not all regions and communities were Muslim, the use and influence of Arabic was varied.
So, Muslim communities adopted the Nastaliq script. And to this day, Urdu is written with Nastaliq. But, Hindu communities continued to use the Devanagari script that originally developed from Sanskrit, the ancestor if Hindustani. This is the first divide between Hindi and Urdu. But, the languages were still the same technically.
Urdu was first mentioned as a dialect of Hindustani with a lot of Persian vocabulary words. Urdu was the lingua franca in the Mughal Empire’s army, and this is also where the language gets its name.
The real divide of the two varieties of Hindustani happened when the British Raj named the Hindustani written with the Nastaliq script the official language. Hindustani speakers who used the original Devanagari script were angered by this choice. A large scale dispute started over which writing system should be the official for the Hindustani language.
The solution was to divide it into Devanagari using Hindi and Nastaliq using Urdu. And that is how the one Hindustani language became Hindi and Urdu.

Hindi vs Urdu Vocabulary
As the political and cultural divide grew between the two versions of Hindustani, the vocabulary changed too. In a conscious effort to separate Hindi from Urdu, Hindi speakers purged the language from the previous Persian influences. In their place, they adopted new Sanskrit vocabulary.
Urdu did the opposite. Sanskrit words were replaced by Persian or Arabic vocabulary. Although this change wasn’t a large scale reform of either language, it certainly reshaped them both. Today, they are still mutually intelligible, but these specific vocabulary differences certainly set spoken Hindi and Urdu apart. And, if you speak either language simply (aka without using big literary words), both Hindi and Urdu speakers will understand you perfectly.
Hindi Letters and Writing System
The Hindi alphabet is a fascinating writing system. Hindi is written in the Devanagari script. This writing system consists of 36 consonants and 11 vowels. Although learning 47 new letters seems scary at first, English native speakers will be glad to know that all of the sounds these letters represent exist in the English language.
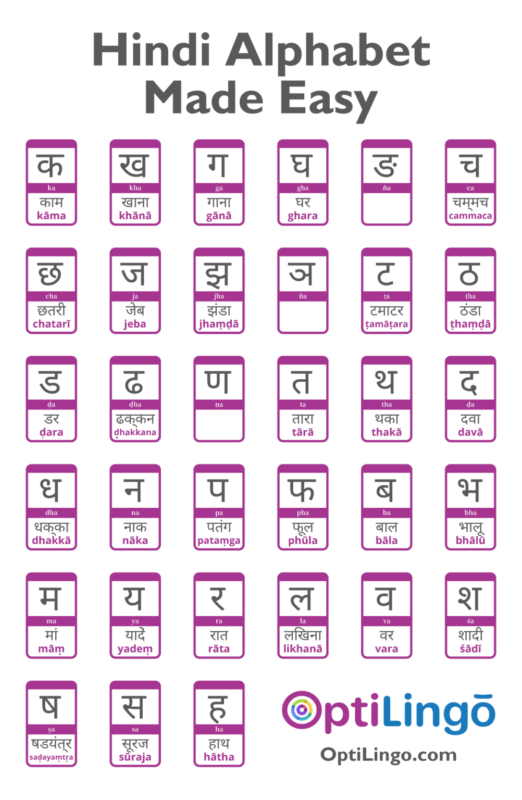
Devanagari is written from left to right, just like English. It’s an alphasyllabary (abugida) writing system, which means that it’s a segmented unit based on the consonant. Consonants and vowels aren’t equal in value. So, consonants in the Hindi writing system carry an inherent vowel, which may change depending on diacritics.
Hindi Consonants.
There are 36 consonants in the Hindi alphabet. The Devanagari writing system recognizes subtle differences in the sound of letters. And the letter order in this script isn’t random. It’s based on strict Devanagari ordering rules, which are based on where you create the sound, and how you say it.
|
STOPS |
NASALS | ||||
| UNVOICED |
VOICED |
||||
|
Unaspirated |
Aspirated | Unaspirated |
Aspirated |
||
| Velar | क | ख | ग | घ |
ङ |
|
Palatal |
च | छ | ज | झ |
ञ |
| Retroflex | ट | ठ | ड (ड़) | ढ (ढ़) |
ण |
|
Dental |
त | थ | द | ध |
न |
| Labial | प | फ (फ़) | ब | भ |
म |
Hindi Vowels
In Hindi, vowels enter the language in two different ways. They’re either signaled by diacritical marks with consonants, or they can also appear individually. Just like consonants, the vowels in Hindi are ordered by the way you pronounce them.
|
ARTICULATION |
VOWELS |
||
|
MONOPHTHONGS |
DIPHTHONGS | ||
|
SHORT |
LONG | ||
|
Guttural |
अ |
आ |
|
|
Palatal |
इ |
ई |
|
|
Labial |
उ |
ऊ |
|
|
Retroflex |
ऋ |
– |
|
|
Palato-Guttural |
ए |
ऐ |
|
|
Labio-Guttural |
ओ |
औ |
|
How to Read Devanagari Script
Although mastering a completely different writing system may seem like a big task at first, but one quality of Devanagari makes reading Hindi relatively simple. The Hindi writing system is entirely phonetic. As you see it written down is how you pronounce it. There are no hidden sounds like in the English word “thorough”.

The Grammar of the Hindi Language
Just like every other language, grammatical rules are very important in Hindi. Let’s break down the grammar of Hindi to see what makes this language unique.
Hindi Cases
Grammatical cases show what role a noun fulfills in a sentence. The Hindi language has three distinct cases:
- direct case
- oblique case
- vocative case
Does Hindi Have Genders?
Yes, the Hindi language has two genders: masculine and feminine. Although this concept doesn’t exist in English, most Indo-European languages have genders. Every object in Hindi is either masculine or feminine. For example, a bus (बस) is feminine, while a room (कमरा) is masculine. But, nouns aren’t the only part of Hindi grammar that’s affected by gender.
Hindi Verbs
In Hindi, you need to be aware of the gender when you’re conjugating verbs. Depending on your gender and the gender of the person you’re speaking to, the verb needs to change. If a verb ends in ई (ii) it’s feminine, and if it ends in आ (aa) it’s masculine. It’s actually a much easier rule than it seems at first.
The verb for “eat” in Hindi is खा (kha). If you’re a man, you’d say खाता (khataa), and if you’re a woman, you’d say खाती (khatii).
Hindi Adjectives
Sometimes, adjectives are also affected by gender in Hindi. But, based on the gender of the speaker instead of the noun it’s attached to. And, luckily, you already know how it changes.
Just like Hindi verbs, you need to add आ (aa) for masculine and ई (ii) for the feminine. But, this doesn’t happen with every adjective.

Hindi Doesn’t Have Articles
In English, we show the definiteness of a noun by adding “the”, “a”, or “an” in front of it. But, the Hindi language doesn’t have this grammatical structure. That’s one lesson you’re welcome to skip!
Hindi Pronouns
Interestingly, the pronouns “he” or “she” doesn’t exist in Hindi. The pronouns in the Hindi language are genderless. But, the verb does change depending on your gender, and the gender of the person you’re speaking to.
Another fascinating aspect of Hindi pronouns comes when you say “you”. There are three ways you can say the personal pronoun “you” in Hindi:
- तु (tuu): very informal, how you address very close friends
- तुम (tum): informal, but you’d address more like work friends, siblings, or spouses this way
- आप (aap): formal, how you’d address your boss, parents, strangers, or elders
You can also use तुम or आप to address plural groups of people.
Hindi Sentence Structure
Unlike English, Hindi is an SOV (subject-object-verb) language. That means that for basic sentences, the verb always comes last.
- I am a teacher. – मैं शिक्षक हूं (main shikshak hoon)
मैं (main) is the first person singular pronoun “I”, and it’s the subject of this sentence. शिक्षक (shikshak) is teacher, and the verb हूं (hoon) “am” is at the very end.
Is Hindi a Hard Language to Learn?
With this many grammar rules, a different writing system, and completely foreign vocabulary, Hindi seems like a hard language to master. But, is that true? Learning Hindi may be easier than you think.
According to the US Foreign Service Institute (FSI), Hindi is a category 4 language. This means that it’s harder to learn than French or German would be for native English speakers. But, it’s also much easier to learn Hindi than Chinese or Japanese. FSI estimates 1100 hours of study to reach Hindi fluency.
Ultimately, there’s no language that’s hard to learn. Only bad language learning methods. If you have the right language learning tool that lets you have fun while constantly helping you progress, learning Hindi won’t be hard.

Is Hindi a Language Worth Learning?
We can give you over 500 million reasons to learn Hindi. As one of the top three most widely spoken languages in the world, learning Hindi is definitely worth it. If you ever plan on living in India, learning its national language is a must.
But, even if you only visit India for vacation, it’s worth learning some essential Hindi vocabulary. Knowing the most common Hindi words and phrases can help you navigate better. You can receive better customer service from grateful locals. And this knowledge also lets you discover this beautiful country in a way no regular tourist can. So, yes, learning Hindi is definitely worth it.
Learn the Hindi Language Easily
In case you’re wondering where that amazing and easy Hindi learning tool is, well it’s actually right here. If you want to achieve Hindi success fast with minimal effort, you need to try OptiLingo.
OptiLingo has the list of the most common Hindi words and phrases. So, it instantly teaches you how to talk to locals. This app isn’t just convenient. It’s also built on scientifically-proven methods. Based on spaced repetition and comprehensible input, it’s an app you can trust to work. Learn Hindi effortlessly by downloading OptiLingo!